Table of Contents
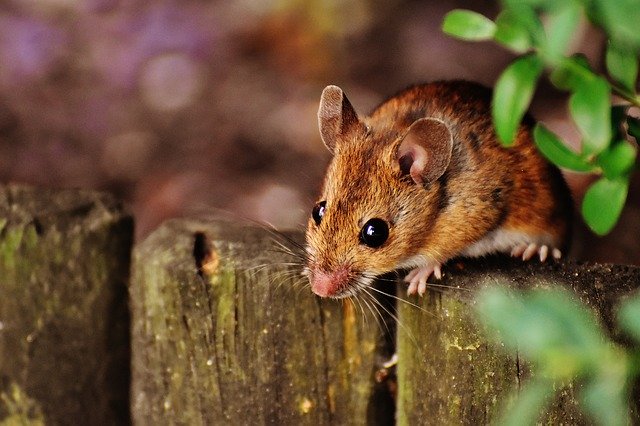
There are two most prevalent rats. First is the Black Rat, also known as the Roof Rat or House Rat. Second is the Norway Rat, also known as the Brown Rat, Water Rat, or Hanover Rat. Each exhibits distinct habits, preferred habitats, and lifespans.
In this post, we’ll address the issue, “How Long Does a Rat Live?”. And we’ll discuss what you can do to assist with rat control.
Bear in mind that rats have two characteristics that make them robust and tough to govern which affects the lifespan of a mouse. These are the two characteristics: survival and prodigious breeding potential. Rats are adept at surviving in limited spaces and propagating their species, and they can stay and reproduce in even the most hostile situations. Let’s take a deeper look at the lifespans of the two most prevalent rat species in the United States.
Average Rat Lifespan
Black Rats’ Lifespan
The Black Rat, sometimes known as the Palm Rat, has a lifetime of around 12 months. That is correct: the Black Rat rarely lives more than a year. As a result, it may be easy to believe that any rat infestation would never endure longer than that. But bear in mind that all rat species reproduce year-round, and a single rat pair can generate hundreds of pups throughout that period.
Indeed, a single female Black Rat may give birth to up to 15 litters every year! That’s a lot of childbirth. Black Rat achieves sexual maturity at the age of 3-4 months. Because of that, they are prolific breeders, which shows how effective these creatures are in propagating their lineage.
Norway Rats’ Lifespan
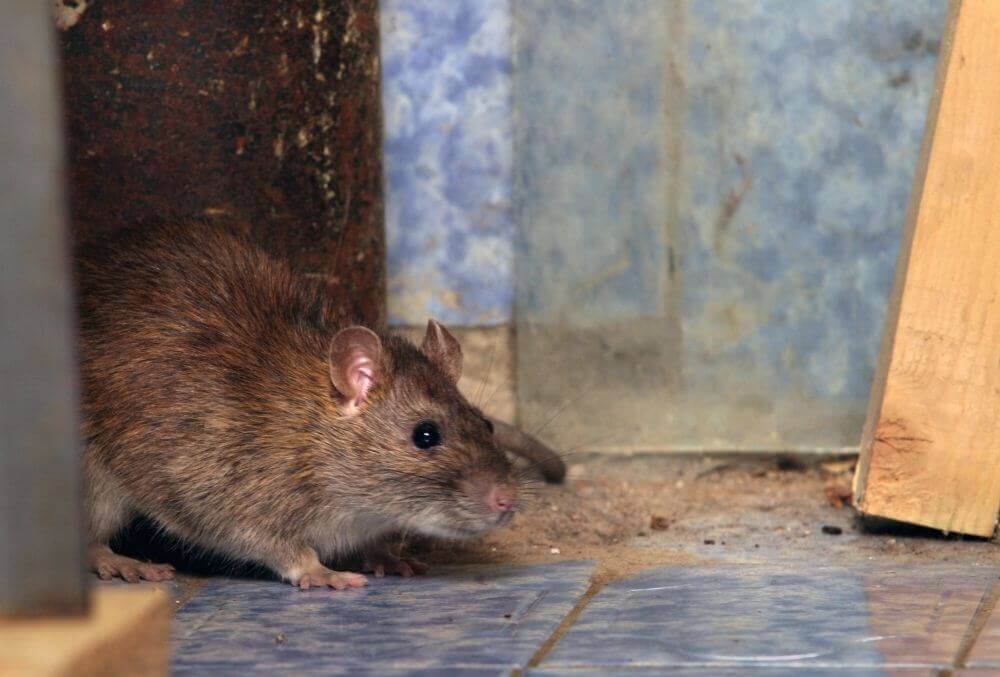
The Norway Rat has a longer lifespan than the Black Rat, almost twice as long. Norway Rats, known as Sewer Rats, have an average lifetime of around two years. Up to 80 percent of Norway Rats are deposited in the sewers when they are only ten weeks old. This number applies to Norway Rats that live in the wild; tamed Norway Rats can live up to four years or even longer.
These two rat species share several characteristics; their lifespans are the most striking. They have similar feeding preferences. But with the exception that the Norway Rat is a hunting rat, and the Black Rat would not hunt even if given the opportunity.
Norway Rat lives more extended than the Black Rat due to its nutritional preferences. Several more factors influence a rat’s lifespan.

Influencers of Mortality
Water and food are the two most crucial parts of a rat’s life, and these two factors will determine whether the rat survives or dies. If the black rat or the Norway rat can gain dependable access to food and water, they will be able to live out their lives. However, if they become ill and unable to get food or water or unable to shelter themselves from the environment, they will perish. That is, assuming they are not eaten first by another animal.
Predation by Rats
Another critical factor affecting a rat’s longevity is whether predators devour the rodent. This factor is a very prevalent cause of early death in rats. This is because the list of natural rat predators is rather extensive. Among the several creatures that seek and consume rats are the following:
- Cats
- Dogs
- Snakes
- Possums
- Weasels
Rats have developed an innate capacity to restrict their exposure to the environment, and this will avoid being eaten by other animals. This situation requires the construction of complicated nests, hunting only at night, and the ability to climb and swim.
Combining water and food with protection from natural predators guarantees that rats will live the longest possible lifetimes.
Influence of Humans
Humans pose a severe hazard to rats as well. After all, we have spent the last 15,000 years fighting rats, and rats have penetrated transport containers, grocery shops, ally every place humans have ever desired to live or consume.
The Black Rat, in particular, has been a constant companion throughout contemporary human history. In many situations, this rat has developed a need for people to survive.
With the long-standing symbiosis with rats, it’s odd that humans are one of their primary predators. The rat war continues to rage with the recent rise in global temperatures.
Conclusion
TIn this blog we have learned how long does a rat live, the Black Rat has a lifetime of around 12 months, but the Norway Rat seldom exceeds two years. They can mate and expand their colony because these two rat species are adept at locating food and concealing themselves.
Even though rats do not live long compared to other animals, their enormous numbers ensure their continuous survival. Rats will continue to fight the human opposition against them as long as they have food, water, and a somewhat secluded spot to raise their progeny.
Rats develop and begin fending for themselves around three weeks after birth. The rodents meet sexual maturity in about five weeks. Then they start mating to generate the next generation, thereby restarting the rat life cycle. Rats have a life expectancy of roughly two to three years. Many rats perish after their first year owing to predation and interspecies fighting.





